02 Git Basics
19 Jan 2021This is a short introduction to one of the most essential tools in software development: a version control system and in particular the Git tool.1
A version control system (VCS) manages files and tracks changes to those files. It stores the complete history and allows you to recover files at any stage of the history (think "undo" to the beginning). Any serious software project uses version control but its uses go beyond software, e.g., documents and data can also be version controlled.
A set of changes is called a commit. It typically contains changes to multiple files. It also contains a timestamp, information about the user who made the changes, and a commit message that explains the changes. The history consists of all the commits. The VCS stores the history in a storage area called a repository.
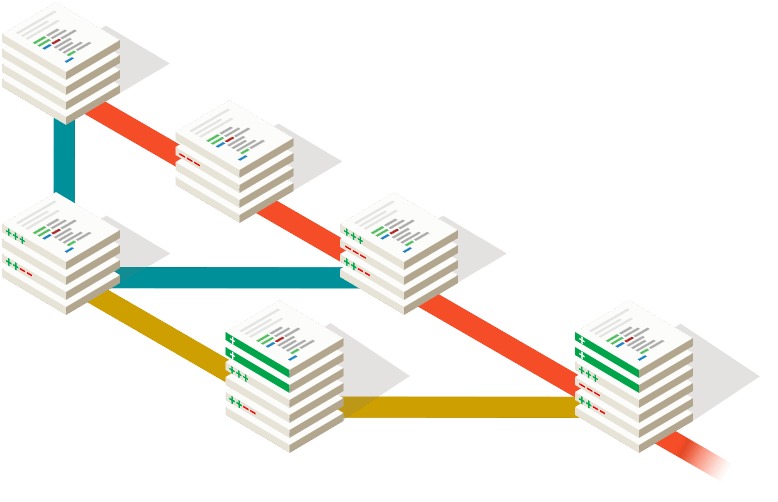
Modern distributed VCS such as Git or mercurial make it easy for multiple developers to work on the same project. They have support for merging changes from different people into a single new file, and for resolving conflicts, i.e., the case when the same part of a file was changed (the changes "collided"). Online platforms such as GitHub, Bitbucket, or GitLab provide free repositories in the cloud (but you don't need these platforms to use a VCS!).
We will use Git. For the class you should get into the habit to version-control your work: in class notes, home works, and projects. You will use GitHub to submit code that you develop as part of your assignments and projects.
- Tutorial
- Set up your own GitHub repositories
- PHY494 Workflow: Resources and Workspace
- Additional reading
Tutorial
Let's use git to manage what we have done so far.
If you want to read more about Git, have a look at the free Pro Git Book by Scott Chacon and Ben Straub and see the other resources.
Configuring Git
The first time you use git you need to tell it who you are: this
information will be the user information in the commit history.
Personalization
Set your name and email.
Use a name and email address that can appear in the clear in the world because you will also use it to sign up and access the GitHub web site; if you are concerned about privacy, please review GitHub’s instructions for keeping your email address private. During this class we will use GitHub all the time:
- Homework will be submitted to private git repositories (only visible to you and the instructors).
- Projects will be submitted to private repositories only visible to you, your team, and the instructors.
- The final project can be submitted to a public repository, visible to everyone in the world (e.g., to use it as part of a portfolio)
Set the name and email associated with your commits (Use your own name and email address!) (and how to color output):
git config --global user.name "Darth Vader"
git config --global user.email "dvader@empire.gov"
git config --global color.ui "auto"There are subtle differences between how Windows and Linux/macOS treat line endings, which matters for programming. Without going into details, please set the following
On Windows
git config --global core.autocrlf trueOn macOS or Linux
git config --global core.autocrlf inputYou can see a list of all your configuration settings with git config
--list.
Git Editor
You also tell what editor to use to write commit messages 2; here we configure atom to be used with git.
Windows
# choose atom as your editor: Windows
git config --global core.editor "C:/Users/USERNAME/AppData/Local/atom/bin/atom.cmd --wait"where USERNAME should be your username. Double check that the path
/c/Users/USERNAME/AppData/Local/atom/bin/atom.cmd really points to
the atom command. (You can try the command which atom, which might
show you the correct path on your computer.) Otherwise, add the correct path. Ask for help if
necessary.
macOS and Linux
# choose atom as your editor: Linux and Mac
git config --global core.editor "atom --wait"git basic command syntax
Git commands always follow the pattern
git <verb> [options] [arguments ...]
In particular, --help is always an option. Also
try git help and git help tutorial.
Creating a repository
A repository starts from a directory with files.
Create your ~/PHY494 directory
During the class you will work on programs. Make a directory
~/PHY494 where you will do your work:
mkdir ~/PHY494Create subdirectories for lessons:
cd ~/PHY494
mkdir 01_shell 02_gitIf you have done the shell exercises then your PHY494 might now look like the following:
~/PHY494/
├── 01_shell
│ ├── Documents
│ │ └── work
│ │ ├── TODO
│ │ └── lesson
│ └── data
└── 02_git
Create a README.md file in 01_shell and 02_git with your
editor that contains text like the
following:
# 01 Shell
Work with the `bash` shell.and
# 02 git
Working with the `git` *version control software*; see https://git-scm.com/.(or write whatever you want — the exact content is not
important). Also create a file ~/01_shell/hello.sh with content
# simple bash script example
echo "Hello World!"Your directory structure should now have two README.md files and hello.sh (you can
use ls -R ~/PHY494 to check):
~/PHY494/
├── 01_shell
│ ├── Documents
│ │ └── work
│ │ ├── TODO
│ │ └── lesson
│ ├── README.md <---- should be present
│ ├── hello.sh <---- should be present
│ └── data
└── 02_git
└── README.md <---- should be present
git init
Turn the PHY494 directory into repository with the git init command:
cd ~/PHY494
git initThat's it. Although, not much happened yet… except, check with
ls -laA new hidden directory ~/PHY494/.git/ appeared. This is your actual
repository (or database) where Git stores all its information. Do
not change anything in this directory (unless you really know what
you are doing) and do not delete the .git directory. If you
delete it, your repository is irrevocably gone (and there is no undo
for that!).
Now try the (possibly) most-used git command:
git statuswhich gives
On branch master
No commits yet
Untracked files:
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
01_shell/
02_git/
… but what does it mean? For this gobbledygook to make sense we need to know about the three stages of git:
The three states of Git
For Git, a file can reside in one of three states
- Modified means that you have changed the file but have not committed it to your database yet; the file is in the working directory.
- Staged means that you have marked a modified file in its current version to go into your next commit snapshot; it lives in the staging area 3.
- Committed means that the data is safely stored in your local
database (the git repository in the
.gitdirectory).
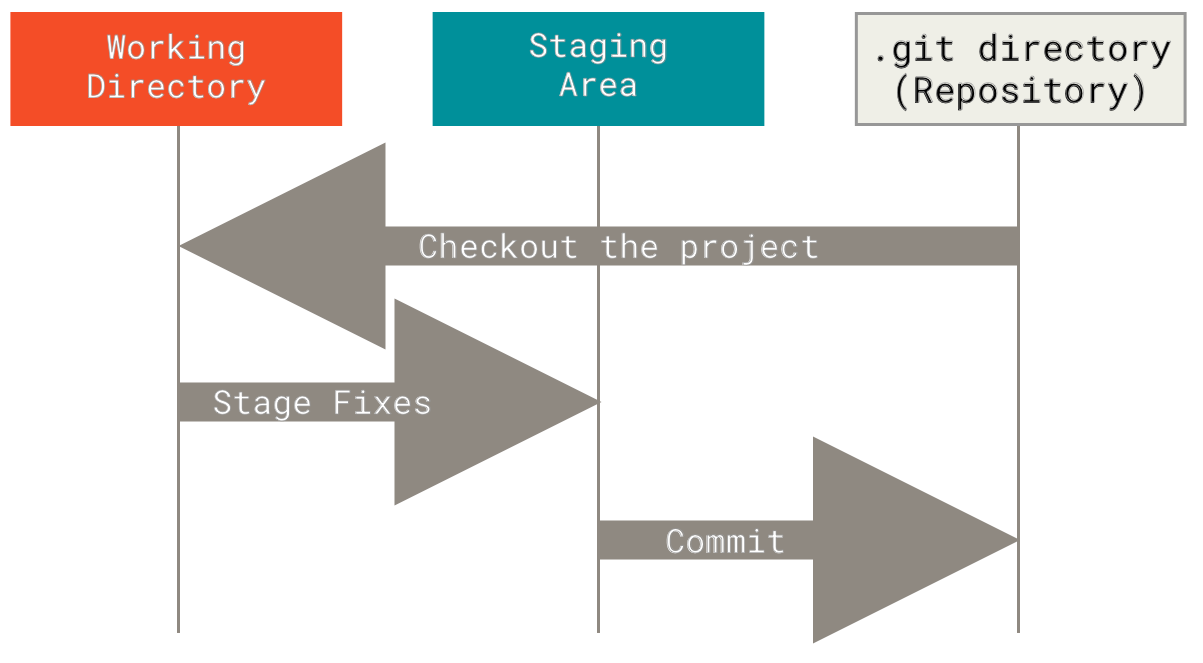
The basic Git workflow:
- modify files in working directory
- selectively stage changes that you want to include in your next commit (adds only those files to the staging area)
- commit your changes (takes files from the staging area and stores them permanently in your Git repository)
Adding files
Prepare the modified files to be committed to the repository: git
add adds files and directories to the staging area:
git add 02_git 01_shell/hello.sh
git statusAdd more files and directories:
git add 01_shell
git status(Use git reset FILENAME to unstage any files that you might have
added accidentally. For instance, do not add backup files that were
created by your editor.)
The files are not committed yet. You can do more work, add more files and directories…
Committing
Check-in (or commit) your changes to your git repository:
git commit- When your editor pops up, enter a commit message: Convention:
- first line (<60 char): one line summary
- second line: blank
- third and following lines: more details The first line is mandatory (you cannot have a commit without a message), the rest is optional. The commit message should succinctly summarize the changes in the commit.
As an example, the following would make a good message:
initial commit of PHY494 class work * lesson 01 on shell * lesson 02 on git - After you wrote and saved the message ("save" in
atom,^Oinnano;ito write andESC :wqto save and exit invim) and exited ("quit" inatom,^Xinnano), your changes will be committed to the repository. - You can also supply the message as an argument:
git commit -m "one line summary of changes". - If you are having problems to make
git commitwith your editor work then instead usegit commit -m 'one line summary message'and debug this problem later.2 - Check the status with
git status…
For a new commit, add files and commit again.
For good measure:
git commitshould show that you have no uncommited changes in your working directory.
History
Git stores complete snapshots of your working tree in the repository: each version (or commit) can be used to recreate an exact state of all your files:
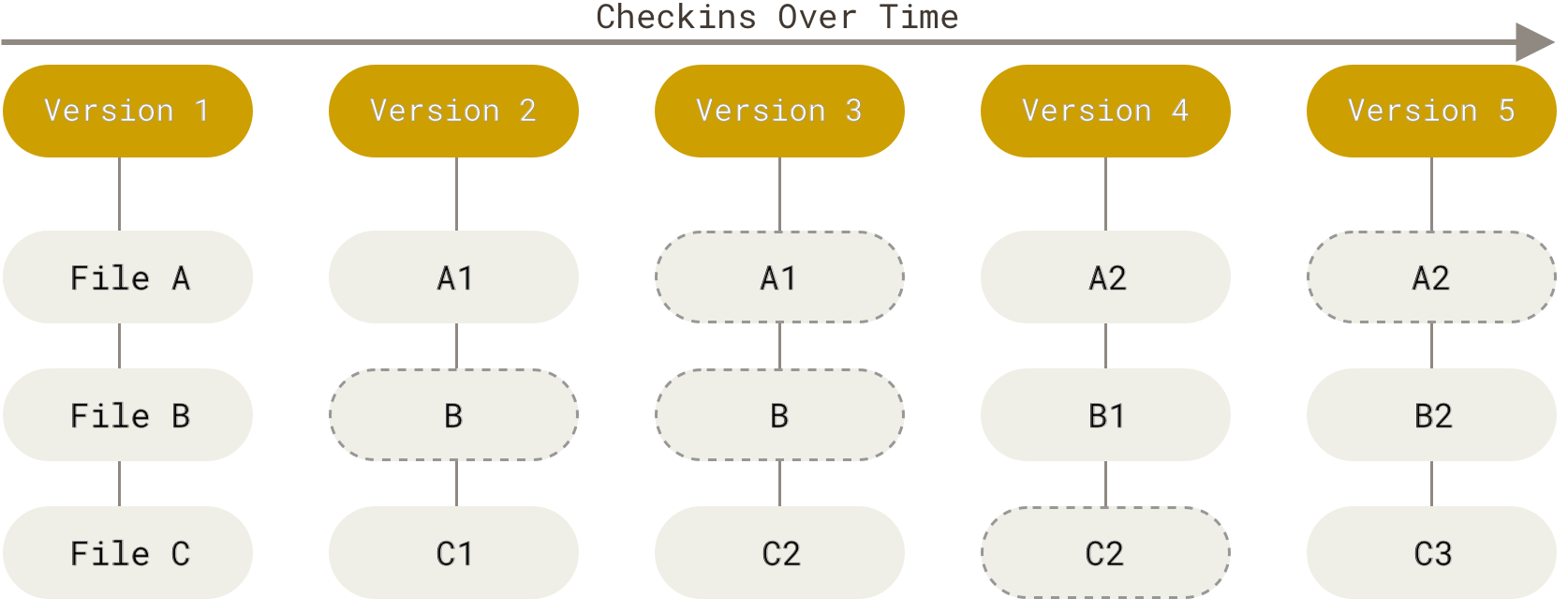
Read the history with
git logRemoving and renaming files
Removing files and directories via git allows you to get them back later.
git rm FILENAME
git rm -r DIRECTORYRenaming is the same as removing the old file and adding the new one but there is also a simple command
git mv OLD NEWThe git rm and git mv commands are similar to the git add
command in that they stage these changes; you still have to
commit them.
Working with remote repositories
Repositories can live in your local file system or remotely on another server ("in the cloud"). Git provides a way to synchronize local and remote repositories.
There's nothing special about remote repositories. They do not really differ from your local repository. Git is a distributed version control system and any repository holds all the relevant history.
There exist many services that host remote repositories "in the cloud". One of them is GitHub (which we use for this class).4
Initializing from remote: git clone
To initialize a local repository from a remote source we use git clone:
git clone URLFor instance, let's clone the class repository where code and data will be posted by the instructor:
cd ~
git clone https://github.com/ASU-CompMethodsPhysics-PHY494/PHY494-resources.git
cd PHY494-resourcesNote:
- The local name of your repository can be any name you like but it is customary (and less confusing) if you go with the default, which is the remote repository name without the ".git" suffix, i.e., PHY494-resources for us.
-
For all other
gitcommands you must be inside your local repository:cd ~/PHY494-resources
Getting changes (reading): git pull
Update your local repository with any "upstream" changes by pulling from the remote repository:
git pullUpdating the remote (writing): git push
If one has write access to a remote repository then one can also update the remote repository with local changes (commits) by pushing all commits that the local repository has:
git push(This will not work for PHY494-resources because only instructors have write access but we will use it below for your own GitHub repositories).
Set up your own GitHub repositories
- Go to https://github.com and create a new account. It is free.5 Remember your GitHub username and the password.
- Create a new repository PHY494 (do not initialize it with a README or other file)
- Note the repository URL https://github.com/USERNAME/PHY494.git
-
Add the remote repository to your local repository
~/PHY494(replace USERNAME with your GitHub username):git remote add origin https://github.com/USERNAME/PHY494.gitWe named the remote "origin", which is a common choice for the main repository. You can have many different remotes, just give them different names. You can list them with
git remote -v -
Traditionally, git used the name "master" for the main branch of the work. However, this name is falling rapidly out of favor so we rename our branch to "main":
git branch -M main(You only have to do this once.)
-
push your local history to the remote repository:
git push --set-upstream origin mainYou need to enter your username and password 6.
You only need the
--set-upstream origin main(or-u origin main) for the first time (it tells git which "branches" to associate with each other in local and remote) 7. All further push operations will then simply begit pushLook at the web interface at https://github.com/USERNAME/PHY494 and see your changes appear.
For the rest of the semester, commit what you did during each class
session to the ~/PHY494 repository on your laptop (and also push
to your GitHub repository as a backup).
Note: Your GitHub repository is for in-class work. Do not commit homeworks there; you will receive private repositories for the duration of the class for this purpose.
PHY494 Workflow: Resources and Workspace
Code, notebooks, and files are being made available on GitHub in the
resources repository
ASU-CompMethodsPhysics-PHY494/PHY494-resources.
For the rest of the semester it will be assumed that you have a
~/PHY494-resources repository that you can update with a simple git
pull as soon as new material is posted.
If you have not done so already, set up ~/PHY494-resources:
cd ~
git clone https://github.com/ASU-CompMethodsPhysics-PHY494/PHY494-resources.gitYou should also have your own workspace repository ~/PHY494 set
up.
Overview
When we start a new lesson you will typically go through the following steps to get code and data files.
- pull latest changes from PHY494-resources
- copy the new directories and files into your workspace PHY494
- work in your workspace
- commit changes in your workspace
- (optional) push changes in your workspace your GitHub repository
Update resources ("pull resources")
Update when your instructor changed anything on the remote:
cd ~/PHY494-resources
git pullCheck what's new
ls -lt(newest at top)
Copy new files and directories to workspace ("copy resources")
You should not be changing anything inside ~/PHY494-resources
(because the next git pull might try to change something that you
did 8) but instead copy whatever you want to change to your own work
directory.
For example:
cp -r ~/PHY494-resources/00_setup ~/PHY494
cd ~/PHY494/00_setupWork, commit, push
Then work on the files in the workspace.
When you have changes that you want to track, git add /
commit / push:
git add .
git commit -m 'updated 00 setup files'
git pushContributing to Open Source on GitHub
GitHub is a provider for remote repositories. It enables you to easily contribute to other projects. This includes
- filing bug reports or feature requests (raising issues); for instance, if you do not agree with some of the Star Wars data from the previous lessons, raise an issue in the issue tracker for the PHY494-auxilliary repository.
- proposing to add your own code and changes through pull requests (but this is too advanced for a our short introduction today — see the additional resources under More…).
More…
- For a longer introductory tutorial see the Software Carpentry lesson on Version Control with Git.
- Resources to learn Git, including cheat sheets.
- Blischak JD, Davenport ER, Wilson G (2016). A Quick Introduction to Version Control with Git and GitHub. PLoS Comput Biol 12(1): e1004668. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004668
- For in-depth discussion read the Pro Git book by Scott Chacon and Ben Straub.
Footnotes
-
Acknowledgements: This lesson uses ideas from Software Carpentry's Version Control with Git and includes an image from Jorge Cham's PhD Comics "FINAL".doc (which is © 2012 Jorge Cham). It also uses images and ideas from git-scm.com (used under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License) and from git-scm.com/book (used under the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial Share Alike 3.0 license). ↩
-
See also Software Carpentry's list of git configuration options for different editors and Associating text editors with Git for details, especially for
atom.For problems with setting up editors in Windows, see the StackOverflow question How can I set up an editor to work with Git on Windows? as a starting point for various recipes. ↩ ↩2
-
Technically, the staging area (or index) is also located in the
.gitdirectory but that is not really relevant. Conceptually, the staging area is different from the Git repository. See more in Git Pro under Gettings Started – Git Basics. ↩ -
Other commonly used git repository hosters are https://gitlab.com and https://bitbucket.org/. ↩
-
An unlimited number of public (i.e., visible for everyone) repositories are free on GitHub but private repositories cost money. However, if you use your school email address (e.g. @asu.edu) you can also get private repositories for free through the GitHub educational discount; see also the GitHub Education site. ↩
-
There are ways to set up remote repositories so that you don't have to provide username and password for every push and which are also more secure. Namely one can use SSH keys instead of the HTTPS protocol, as described in the GitHub tutorial on Generating SSH keys. ↩
-
Branching is a more advanced topic, which is explained in the materials linked under More…. We barely scratched the surface of Git but this will be sufficient to already make good use of this very powerful tool. ↩
-
If you happen to have accidentally edited files inside
~/PHY494-resourcesyou might run into merge conflicts when you rungit pullthe next time. If that happens, copy all files that you edited (usegit statusto see which ones are modified) to a safe directory and then reset with the commandcd ~/PHY494-resources # Next command only if you ran into a merge conflict # during a 'git pull' git merge --abort # undo ALL of YOUR changes git reset --hard HEADWARNING: This will undo all your changes but will allow you to just run the next
git pullcommand again without problems. ↩